Effective Ways to Modify Your Gastroparesis Diet for Better Digestion in 2025
Managing gastroparesis effectively involves a careful and thoughtful gastroparesis diet that caters to individual needs. The concept of a healthy diet for those with gastroparesis centers around ease of digestion and nutritional proficiency. This article guides you through practical modifications you can make to your gastroparesis meal plan in 2025, fostering better digestion and overall health.
Understanding Gastroparesis and Dietary Adjustments
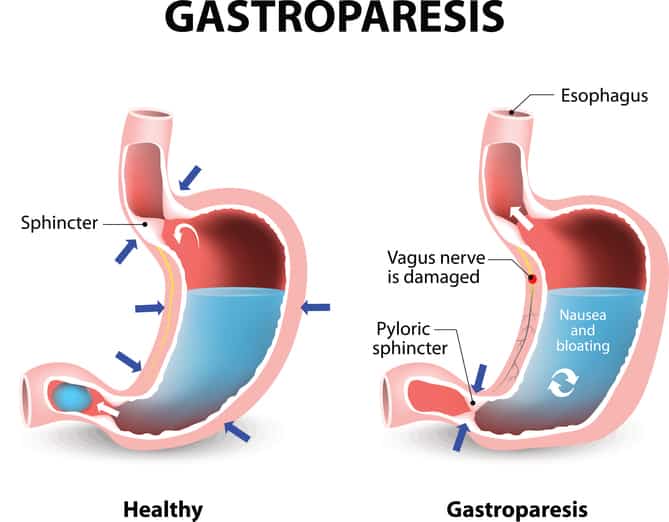
Gastroparesis is a condition characterized by delayed gastric emptying, leading to various digestive challenges. Modifying your diet can significantly influence symptoms such as bloating, nausea, and early satiety. Emphasizing easy to digest foods, high protein meals, and small frequent meals can help in managing these symptoms effectively. The goal is to create a dietary framework that aligns with your body’s needs while embracing tasty and satisfying options.
The Role of Low Fiber Diets
One key adjustment in managing gastroparesis is adopting a low fiber diet. High-fiber foods can be hard to break down, exacerbating symptoms. Instead, focus on foods that are softer and easier on the digestive system. Options such as white rice, plain pasta, or ripe bananas provide essential energy without overwhelming the stomach. As you plan your meals, include a variety of soft foods while understanding which fibrous items might trigger discomfort.
Meal Timing and Frequency
Incorporating meal timing strategies can further support digestive health. Consuming small frequent meals instead of large meals helps to manage fullness and prevents overexertion of the digestive system. Aim for six small meals throughout the day, ensuring each is rich in important nutrients. By spread out your meals, you may see an improvement in both symptom management and energy levels.
Hydration and Liquid Nutrition
Hydration plays a vital role in digestion. Incorporate liquid nutrition as part of your daily intake—smoothies and soups can be nutrient-dense while remaining easy to consume. Additionally, consider hydration strategies by adding electrolyte-rich drinks, which helps with nutrient absorption. Always consult with a healthcare professional to ensure your hydration needs align with your overall health.
Food Choices and Nutritional Strategies
Your choices in food can make a significant difference in how you manage gastroparesis. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods while being mindful of your intake, you can optimize your diet effectively. Key elements to consider include carbohydrate management and avoiding foods that aggravate symptoms. This knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions about your meals.
Nutritional Supplements and Their Benefits
Depending on your individual needs, integrating vitamin supplementation can ensure you meet your nutrient requirements without overwhelming your digestive system. This is especially important if your diet is compromised due to symptoms. Supplements like vitamin B12, vitamin D, and electrolyte solutions can greatly benefit symptom management. Always discuss any supplementation with a healthcare provider to customize your approach effectively.
Cooking Techniques for Gastroparesis
Adopt cooking techniques that keep food easy to digest. Steaming and pureeing are excellent ways to create gastroparesis safe foods. Using a slow cooker can enhance flavors while making food softer, which may aid digestion. Discover recipes specifically designed for beverage or sheer consistencies; this adaptation can provide balance in flavors while also presenting meal options that are easy to consume.
Foods to Avoid
Understanding foods to avoid is equally important in your dietary strategy. High-fat and spicy foods can trigger discomfort and nausea. Dairy products might also cause issues for some individuals. Document your meals in a food diary, tracking what you consume, to identify potential problematic foods and avoid them in the future. This practice will help in enhancing overall digestion and comfort.
Planning and Meal Prep for Success
Effective meal planning is essential to navigating a successful diet for gastroparesis. Utilizing a gastroparesis meal plan allows you to structure your intake around your lifestyle, ensuring you are set up for success without unnecessary stress. Including versatile recipes and quick prep ideas will facilitate adherence while maintaining a balanced diet.
Meal Prep Ideas and High-Calorie Snacks
To support caloric needs, consider high-calorie snacks such as nut butters or Greek yogurt, both of which are nutrient-rich options. Preparing these foods requires minimal effort and can be stored easily. Include these snacks in your meal plan to maintain fuel levels throughout your busy day, enhancing energy without impeding digestion.
Tracking Progress and Adjusting Diet
Implementing a food tracking system offers valuable insights into how various foods impact your symptoms. Noticing patterns in your digestive response allows for timely adjustments to your meal plan. Regularly meet with your healthcare provider to help calibrate your dietary approach, ensuring it aligns with your long-term management goals.
Monitoring Gut Health With Probiotic Foods
Incorporating probiotic foods like yogurt and kefir can augment digestive health. These foods replenish healthy gut bacteria, which may enhance digestion and address symptoms of gastroparesis. Explore recipes that creatively incorporate these options into your daily meals while staying conscious of personal tolerance and comfort levels.
Conclusion and Summary of Key Points
In 2025, we have the opportunity to better manage gastroparesis through mindful dietary changes and practical approaches. To summarize, focus on integrating small frequent meals, easy to digest foods, low fiber diets, and proper hydration in your gastroparesis diet. Utilize high-calorie snacks, monitor symptoms through food tracking, and consider collaboration with healthcare professionals on supplementation and planning to better streamline your individualized strategy.
FAQ
1. What are some easy to digest foods for gastroparesis?
Great options for easy to digest foods include white rice, bananas, applesauce, and cooked carrots. These items not only provide essential nutrients but also reduce strain on your digestive system. Incorporating low-fat foods can also enhance meal pleasantness without risk of complications.
2. How can I manage my meals if I have gastroparesis?
To manage meals with gastroparesis, consider adopting a gastroparesis meal plan that includes high protein meals. Plan ahead by making meals in batches and store them in portion sizes for convenient access. Additionally, utilizing mealtime strategies, such as focusing on smaller meals throughout the day, helps reduce symptoms associated with delayed gastric emptying.
3. How do I ensure proper nutrient intake on a low fiber diet?
When following a low fiber diet for gastroparesis, focus on nutrient-dense foods, like eggs, smooth nut butters, and lean meats, to ensure enough vitamins and minerals. Supplements may also play a vital role; consult a healthcare provider to customize options that address potential gaps in your nutrition management.
4. Can hydration help with gastroparesis symptoms?
Yes, proper hydration can aid in alleviating gastroparesis symptoms by supporting digestion and preventing discomfort. Aim to incorporate fluids into your meals and choose liquid nutrition options for more effective intake. Electrolyte drinks can also be beneficial—prioritize staying hydrated to promote better digestive function.
5. What foods should I avoid with gastroparesis?
Foods that should typically be avoided include high-fat and spicy items, as well as dairy if you’re sensitive to lactose. Identifying foods that aggravate symptoms is crucial; maintain a food diary to track what works best for you and collaborate with healthcare professionals for tailored recommendations.