Effective Ways to Manage Hypoglycemia Diet for Better Health in 2025
Managing a hypoglycemia diet is essential for individuals aiming for better health in 2025. Proper nutrition not only aids in maintaining stable blood sugar levels but can also enhance overall well-being. With a better understanding of food combinations, timing, and portion control, one can effectively navigate the challenges of low blood sugar and its symptoms. This article delves into practical strategies for creating an effective diet plan, tailored to managing hypoglycemia effectively.
Understanding Glycemic Response
The glycemic index (GI) plays a critical role in the context of a hypoglycemia diet. Foods categorized with low GI values are absorbed more slowly, leading to gradual increases in blood sugar levels, which is essential for preventing sudden drops. Conversely, foods with high GI indices can lead to quick spikes in blood sugar followed by steep declines, triggering hypoglycemic episodes. Recognizing the impact of your food choices on glycemic response is crucial for maintaining blood sugar stability. Incorporating low glycemic foods, such as whole grains and legumes, can help sustain energy levels through the day.
Balanced Meals for Hypoglycemia
Creating balanced meals for hypoglycemia involves combining different food groups to stabilize blood sugar effectively. A nutritious meal should contain a balance of protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats. For example, a meal with grilled chicken (protein), quinoa (complex carbs), and steamed broccoli (vegetables rich in fiber) can promote longer satiety and prevent blood sugar dips. Moreover, keep in mind that incorporating diverse food colors on your plate not only makes meals more appealing but also ensures a range of nutrients vital for health and metabolic processes.
Meal Timing for Hypoglycemia
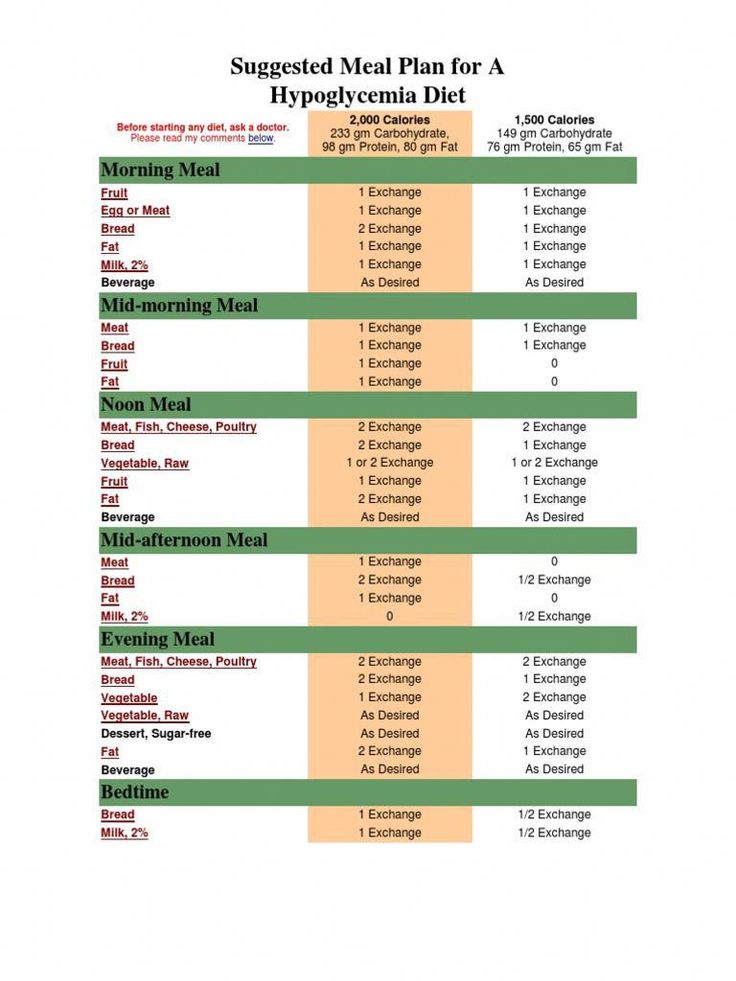
Timely consumption is vital in a hypoglycemia management plan. Eating small, frequent meals can help stabilize blood sugar levels in those prone to hypoglycemic symptoms. For an ideal approach, opt for three main meals complemented by two to three small snacks throughout the day. It’s also important to monitor portion control; serving sizes directly influence blood sugar reactions. Establishing a consistent eating schedule not only trains your body to expect nourishment at certain times but also enhances the effectiveness of your dietary strategies.
Nutritious Foods to Incorporate
When managing a diet plan for hypoglycemia, it’s crucial to know which foods to embrace. Focusing on nutrient-dense options can alleviate the risk of low blood sugar levels. Incorporating wholesome low blood sugar foods such as vegetables, whole grains, high-quality proteins, and fiber-rich fruits can promote better energy regulation. Superfoods like avocados, nuts, and flaxseeds are especially beneficial due to their healthy fats and protein content, providing sustained energy and mitigating blood sugar fluctuations.
Proteins and Fiber in Hypoglycemia Diet
Both protein and fiber play significant roles in a hypoglycemia diet. Including lean protein in every meal helps slow digestion and promote blood sugar stability. Options such as chicken, fish, beans, and tofu can be excellent additions. Additionally, fiber-rich foods, including oats, berries, and leafy greens, help slow the absorption of sugars into the bloodstream. For instance, a breakfast of oatmeal garnished with almonds and berries not only supports energy but also contributes to digestive health.
Healthy Snacks for Blood Sugar Control
Choosing appropriate snacks can safeguard against dips in blood sugar. Options like Greek yogurt, nuts, or a piece of whole fruit can be excellent choices. Creating snacks that combine protein, fiber, and healthy fats, such as apple slices with almond butter, can help manage cravings and maintain energy. Staying prepared with well-portioned snacks can prevent the temptation to reach for sugary processed alternatives, thereby protecting against fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Nutrition and Lifestyle Changes for Hypoglycemia
For effective hypoglycemia management, incorporating lifestyle changes alongside dietary adjustments is key. This includes maintaining regular physical activity, staying hydrated, and employing stress-reducing techniques. Exercise can increase insulin sensitivity, helping manage blood sugar levels more effectively. Furthermore, monitoring hydration and ensuring optimal intake of fluids can directly influence blood sugar stability. Prioritizing sleep and recovery is also essential, as lack of sleep can exacerbate blood sugar irregularities.
Managing Stress and Its Impact on Blood Sugar
Stress significantly affects blood sugar levels, necessitating strategies for managing stress and emotional well-being. Engaging in mindfulness techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises, can alleviate stress and contribute to overall health. Additionally, understanding the relationship between mood swings and blood sugar can lead to better reactions during challenging periods. Keeping a health journal may help identify patterns between stress and low blood sugar, ultimately promoting proactive management strategies.
Hydration and Blood Sugar Stability
Staying properly hydrated is a significant yet often overlooked aspect of managing a hypoglycemia diet. Water helps the body maintain optimal glucose regulation, while proper hydration aids digestion and nutrient absorption. Aim for 8-10 cups of water per day and consider factors such as exercise or heat, which may increase hydration needs. Consistently drinking water can also help with reducing cravings and preventing snack indulgences that may lead to blood sugar spikes or drops.
Practical Tips for a Successful Hypoglycemia Diet
Implementing a hypoglycemia diet involves more than just understanding food: it requires a personalized approach tailored to the individual’s needs. Here are practical tips to enhance your dietary plan:
- Track your blood sugar levels regularly to identify patterns and triggers.
- Prioritize the creation of a food diary to record emotional and physical reactions to different foods.
- Participate in meal planning activities to ensure a balanced approach to dietary needs.
- Be mindful of eating environments and make adjustments in social settings to avoid unwanted spikes.
- Consult with healthcare professionals to adjust medications if dietary changes are needed.
Key Takeaways
- Focus on incorporating low GI foods and balance between proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
- Maintain regular meal timing and stay hydrated to ensure balanced blood sugar levels.
- Implement practical tips and lifestyle changes to improve overall well-being and stress management.
- Monitor and adjust based on individual responses and healthcare advice.
FAQ
1. What foods are best for managing hypoglycemia?
Foods rich in protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats are ideal for managing low blood sugar. Examples include whole grains, nuts, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables. It’s important to choose healthy snacks for hypoglycemia that can provide sustained energy without causing spikes.
2. How often should I eat to prevent hypoglycemic episodes?
Eating smaller meals more frequently can help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Aim for three main meals and two to three snacks per day to prevent hypoglycemic episodes. Consistency in timing is also crucial to help your body regulate glucose effectively.
3. Can drinking water influence my blood sugar levels?
Yes, proper hydration is essential for maintaining blood sugar stability. Dehydration can lead to imbalanced glucose levels and may trigger hypoglycemic symptoms. Ensure you’re drinking enough water throughout the day for overall health.
4. What role does fiber play in a hypoglycemic diet?
Fiber slows the digestion of carbohydrates, which helps in preventing rapid spikes and drops in blood sugar levels. Incorporating fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is beneficial for blood sugar stability.
5. How can I manage cravings while on a hypoglycemia diet?
Managing cravings can be achieved by ensuring balanced meals that contain adequate amounts of protein and fiber. Regular snacks for blood sugar control can help stave off hunger and provide necessary energy, reducing the likelihood of indulging in unhealthy foods.
6. What are some good meal prep ideas for hypoglycemia management?
Meal prepping can include dishes like quinoa salads, grilled chicken and vegetables, and overnight oats. These options promote nutritional awareness and allow easy access to balanced meals throughout the week, ultimately supporting blood sugar regulation.
7. How does regular exercise contribute to managing hypoglycemia?
Regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, improves glucose regulation, and helps maintain steady energy levels. Incorporating some form of physical activity daily can play a crucial role in managing hypoglycemia and promoting better health overall.