“`html
Comprehensive Guide to 1-3 Month Pregnancy Diet: Essential Foods for a Healthy Start in 2025
The first trimester is a critical time in a woman’s pregnancy journey. During this phase, **nutrition** becomes paramount for both the mother and the developing fetus. This article explores the importance of a balanced pregnancy diet in the first trimester, focusing on various nutritious foods for pregnancy that contribute to a healthy start. We will cover meal plans, essential nutrients, safe foods, and practical tips to help manage the unique dietary needs of expecting mothers in 2025.
Building a Balanced First Trimester Diet
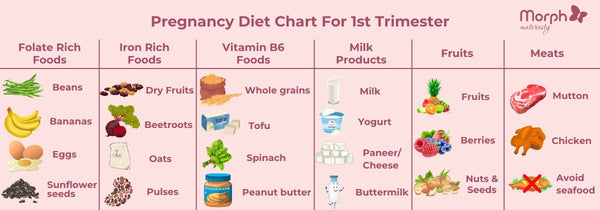
Establishing a balanced first trimester diet is crucial for fetal health. This period requires an emphasis on consuming nutrient-rich foods that support both growth and development. It is important to include diverse food groups to ensure adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals, such as folic acid and iron-rich foods. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, proteins, whole grains, and dairy will lay the foundation for a healthy pregnancy meal plan.
Essential Nutrients for Fetal Development
There are several key nutrients that expectant mothers must prioritize in their pregnancy meal plan. These include folic acid, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. Folic acid is vital for reducing the risk of neural tube defects; hence, foods like leafy greens and fortified cereals should be staples. Iron-rich foods, such as lentils and red meat, can prevent anemia in pregnant women. Calcium supports the mother’s bone health and the baby’s skeletal development, with dairy products, nuts, and green vegetables being excellent sources. In addition, incorporating omega-3 fatty acids from seafood and flaxseeds aids neurological development.
Healthy Sources of Protein and Whole Grains
Protein is an integral part of a healthy pregnancy diet. Lean meats, fish, eggs, beans, and dairy contribute to the increased protein needs during pregnancy. Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread, provide essential carbohydrates that fuel the mother’s increased energy requirements. A focus on whole foods enhances **meal frequency during pregnancy**, ensuring that the mother receives small and frequent meals throughout the day to help maintain energy levels and minimize nausea.
Incorporating Hydration and Healthy Fats
Hydration is another vital aspect of prenatal nutrition. Drinking adequate water helps to manage pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and fatigue. It’s advisable for expecting mothers to aim for at least 8-10 cups of fluids daily. Moreover, including healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil can support the baby’s brain development while providing needed calories, making it a critical component of the pregnancy diet.
Meal Planning Tips for the First Trimester
Effective planning can simplify the process of adhering to a healthy first trimester diet. Meal prep allows pregnant women to ensure they have access to the nutritious foods they need while minimizing stress. Preparing meals in advance can also help address those frequent \textbf{pregnancy cravings} and manage nausea more effectively.
Creating a Pregnancy Grocery List
When shopping for the essential foods for your first trimester, create a pregnancy-specific grocery list. Include a variety of fruits like bananas and berries, vegetables such as broccoli and carrots, protein sources like chicken and beans, and whole grains. Additionally, incorporating healthy snacks like yogurt and nuts can help combat hunger and maintain energy levels throughout the day. Making a grocery list can also aid in maintaining budget-friendly shopping practices.
Meal Ideas and Recipes
Crafting easy pregnancy recipes can encourage healthy eating habits. Breakfast might include oatmeal topped with berries and nuts, while lunch can be a quinoa salad with cherry tomatoes and chickpeas. A nutritious dinner option could be grilled salmon with steamed veggies and brown rice. Snack ideas include apple slices with almond butter and carrot sticks with hummus. Utilize resources that provide nutritious breakfast ideas for pregnancy to achieve balanced meals throughout the day.
Tips for Managing Nausea with Food
Morning sickness can be challenging. To help manage nausea, it can be beneficial to keep food options nearby for when cravings strike. Eating small, frequent meals instead of large ones can also help ease nausea. Ginger-infused teas and crackers can be beneficial for some women as natural remedies. Staying hydrated is crucial during this time, and many women find that ginger ale or mineral water can help in relieving discomfort.
Important Dietary Considerations
A healthy pregnancy diet not only supports fetal development but can adress various concerns during pregnancy, including weight management, food allergies, and dietary restrictions. Understanding the individual’s nutritional needs fosters a supportive environment for both mother and child.
Addressing Food Allergies and Dietary Restrictions
Women with existing food allergies or those following specific diets, such as a vegetarian pregnancy diet, should approach their diet thoughtfully. Opting for vegetarian sources of protein—like tofu, nuts, and legumes—can ensure adequate nutrient intake. Learning about safe pregnancy foods and avoiding highly processed foods plays a crucial role in maintaining a balanced diet while supporting the baby’s health.
Coping with Emotional Eating
Pregnancy can be an emotional rollercoaster, often resulting in cravings or emotional eating. Understanding coping mechanisms to manage emotional eating is important for maintaining a healthy weight during pregnancy. Engaging in hobbies, exercising gently, and seeking community support can lower the chances of stress-induced eating behaviors. Identifying trigger foods can also facilitate mindful eating during pregnancy.
Nutrition Myths Debunked
Misconceptions about pregnancy nutrition abound. It’s essential to provide factual information regarding safe caffeine intake and other dietary aspects. For instance, while many believe they should “eat for two,” the focus should be on nutrient density rather than simply increased portions. Educating oneself on nutritional needs during pregnancy and seeking advice from healthcare providers can alleviate confusion and promote healthy eating habits throughout this time.
Key Takeaways
- Focus on a nutrient-rich pregnancy diet featuring fruits, vegetables, proteins, and whole grains.
- Create a grocery list tailored to meet the diverse dietary needs of pregnancy while considering food allergies and preferences.
- Implement meal prep strategies to ease the transition into healthy eating and manage pregnancy symptoms effectively.
- Address emotional eating by recognizing triggers and fostering supportive communities.
- Stay informed about nutritional myths and prioritize education surrounding prenatal dietary guidelines.
FAQ
1. What are some safe seafood options during pregnancy?
When choosing seafood during pregnancy, options like salmon, shrimp, and catfish are safe and beneficial. It’s essential to avoid high-mercury fish like shark, swordfish, and king mackerel. Aim for two servings of low-mercury seafood weekly, focusing on omega-3 rich varieties that support fetal brain development and overall health.
2. How can I increase my hydration during pregnancy?
To enhance hydration, aim to drink at least 8-10 cups of water daily. Incorporating hydrating foods, such as cucumbers, oranges, and melons, can also contribute to fluid intake. Additionally, herbal teas can be a hydrating alternative, working well to maintain hydration levels without caffeine.
3. What are some low sugar foods I can include in my diet?
Incorporating natural low-sugar foods, such as whole fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, is vital during pregnancy. Avoiding processed snacks and beverages with added sugars is recommended, as they can lead to unnecessary weight gain and potential health concerns.
4. Are there special nutritional considerations for vegetarian pregnancies?
Vegetarian pregnant women should focus on addressing their protein needs with options like lentils, beans, nuts, and dairy, ensuring they consume sufficient iron, calcium, and vitamins B12 and D. Supplementation may be necessary if dietary intake is insufficient to prevent deficiencies.
5. How can I manage cravings healthily?
Managing cravings in a healthy manner involves understanding them as a normal aspect of pregnancy. Aim to satisfy cravings with healthy alternates and ensure they encompass nutrient-rich foods. For instance, if craving sweets, opt for fruit or yogurt. Maintaining a balanced nutrition plan helps mitigate excessive indulgence.


“`