Smart Guide to Low FODMAP Diet
The Low FODMAP diet is a scientifically-backed approach designed to alleviate digestive distress caused by certain fermentable carbohydrates. It is particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from conditions such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and other digestive disorders. This article will provide proven meal plans for 2025 success, alongside comprehensive insights into low FODMAP foods, grocery lists, cooking tips, and the overall benefits of adopting a low FODMAP lifestyle.
Understanding the Low FODMAP Diet
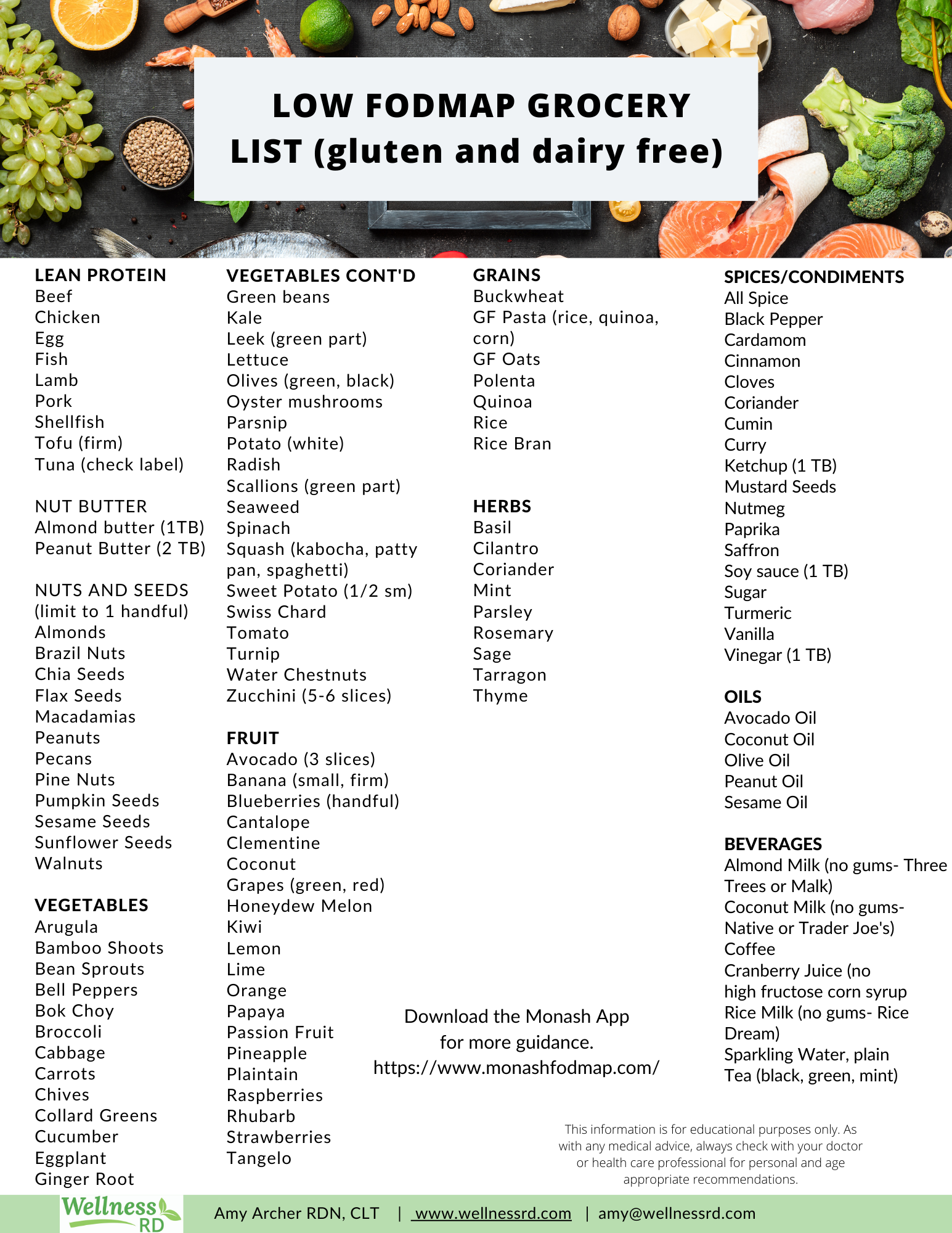
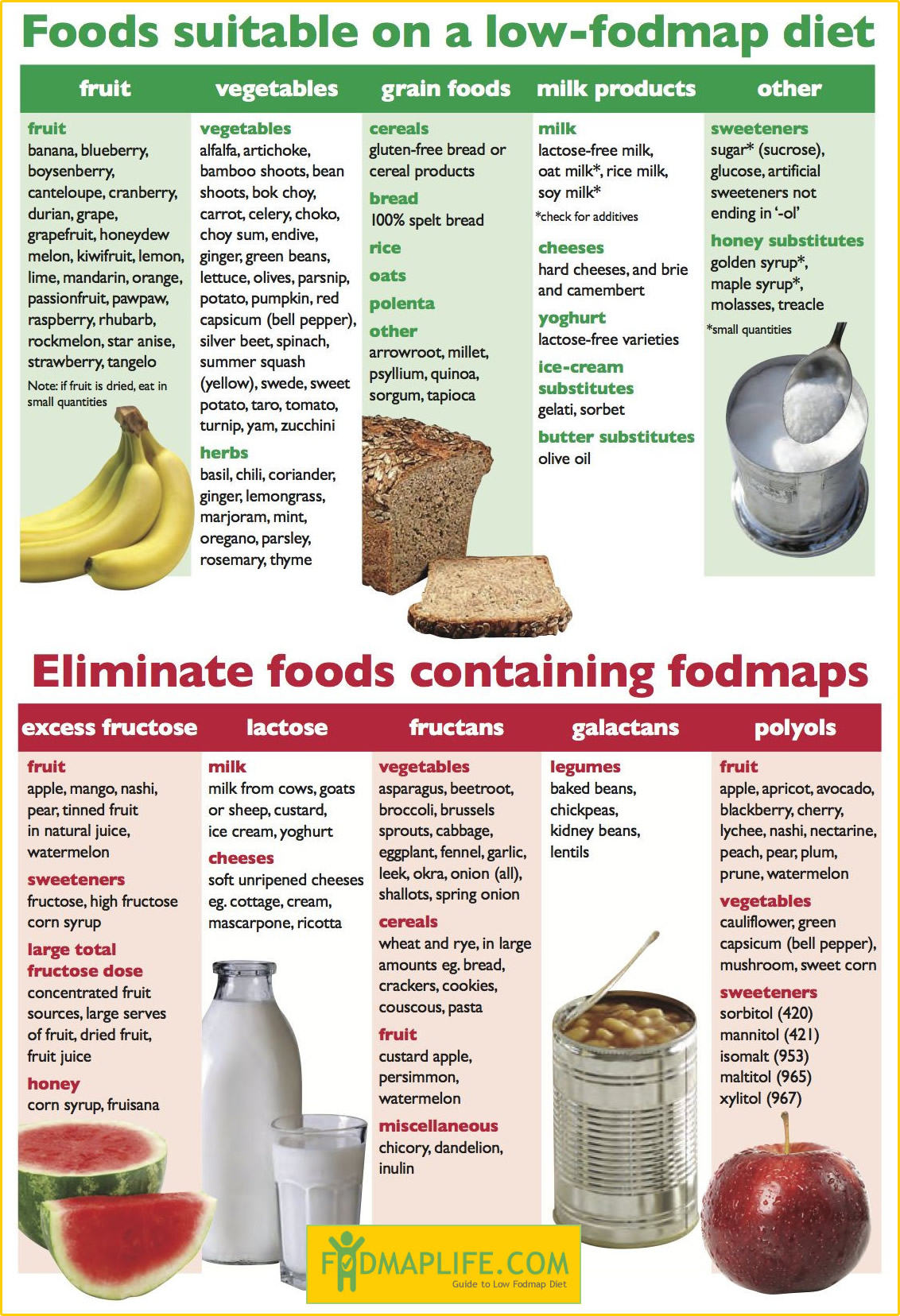
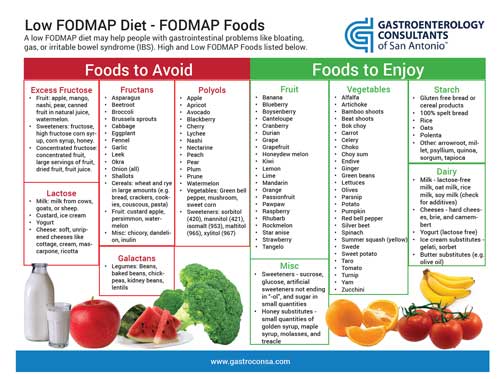
The foundation of the low FODMAP diet lies in understanding what FODMAPs are and how they affect gut health. FODMAP is an acronym for ferments oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols. These carbohydrates can be poorly absorbed in the small intestine, leading to symptoms like bloating, gas, and abdominal discomfort in sensitive individuals. By eliminating high FODMAP foods, you can assess your tolerance and improve your digestive health.
What is a Low FODMAP Diet?
A low FODMAP diet involves restricting foods that are high in fermentable carbohydrates for a period of time—typically four to six weeks—followed by a gradual reintroduction phase to identify personal triggers. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to navigate this structured approach safely. The goal is to achieve symptom relief while ensuring nutritional balance. This dietary management is particularly effective for IBS and other gut health issues, making it an increasingly popular choice today.
Benefits of Following a Low FODMAP Diet
Research indicates that the low FODMAP diet can significantly reduce symptoms related to IBS and other gastrointestinal disorders. People often report improved digestion and reduced bloating after adhering to the diet. Studies show that nearly 70% of individuals with IBS experience symptom relief when they eliminate high FODMAP foods from their diet. By focusing on low FODMAP foods, you not only alleviate discomfort but also enhance your overall dietary choices by embracing healthier options.
Meal Plans and Preparation
Creating a well-structured meal plan is crucial for success on the low FODMAP diet. This section will detail easy-to-follow meal plans, including breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks, paired with valuable tips on meal prepping and organization.
Low FODMAP Meal Ideas for Beginners
For those just starting the low FODMAP diet, it’s beneficial to compile a list of low FODMAP meal ideas. Breakfast options can include oatmeal topped with lactose-free yogurt and blueberries, while a simple lunch might feature grilled chicken salad with spinach, cucumbers, and a lemon vinaigrette. For dinner, stir-fried vegetables with quinoa and tofu offer a satisfying, nutritious meal. Selecting diverse options helps prevent dietary boredom and improves adherence.
Low FODMAP Snacks and Treats
Snacking can be tricky but knowing low FODMAP snacks can keep your energy up without triggering digestive issues. Good options include carrot sticks with hummus made from canned chickpeas, rice cakes with peanut butter, or dark chocolate as a sweet treat. It’s essential to read labels as some items may contain hidden high FODMAP ingredients.
Meal Prep Strategy for Low FODMAP Success
Effective meal prep is a game-changer for success on the low FODMAP diet. Plan your week’s meals ahead of time, utilizing a low FODMAP grocery list that emphasizes fresh proteins, vegetables, and gluten-free grains. Preparing meals in advance not only saves time but also ensures that you have compliant options readily available when hunger strikes. Containers with portions can help with portion control and can make tracking your low FODMAP intake easier.
Cooking Tips for Low FODMAP Dishes
Cooking on a low FODMAP diet doesn’t mean sacrificing flavor or creativity. This section will explore vital cooking techniques and ingredient swaps that can make low FODMAP cooking satisfying and delicious.
Low FODMAP Substitutes for Baking
Baking is entirely feasible on a low FODMAP diet, with many substitutes available. Use gluten-free flour blends to replace standard wheat flour and almond milk or lactose-free milk for traditional dairy. Brown sugar can substitute for sweeteners containing high levels of FODMAPs. For sweetness without FODMAPs, try coconut sugar or maple syrup in moderation.
Low FODMAP Sauces and Seasonings
Sauces can add depth to your dishes but check for hidden high FODMAP ingredients. Opt for homemade low FODMAP sauces made with lactose-free butter, olive oil, and fresh herbs. For flavor, use spices like cumin, paprika, or ginger which are generally low in FODMAPs. When dining out, inquire about the ingredients in sauces, emphasizing options that are clear of troubling components.
Low FODMAP Cooking Techniques
Employing varied cooking methods can keep meals exciting on a low FODMAP diet. Grilling, steaming, and roasting can enhance the natural flavors of low FODMAP foods. Season vegetables beautifully and try different grain pairings such as millet or quinoa to mix it up. Adjusting your cooking style promotes vibrant flavors while conforming to diet guidelines.
Dining Out on a Low FODMAP Diet
Finding low FODMAP restaurant options can be a challenge but not impossible. Knowing how to communicate dietary needs is key. This section covers navigating restaurant menus while adhering to low FODMAP principles.
Low FODMAP Tips for Eating Out
When dining out, approach menus with an informed strategy for success. Look for dishes centered around grilled or roasted proteins with a side of non-starchy vegetables. It’s helpful to ask if they can adjust meals to remove high FODMAP ingredients such as garlic or onions and add flavor with herbs instead. Many restaurants are accommodating if you’re transparent about your dietary requirements.
Low FODMAP International Foods
Experiencing world cuisine is still possible with a low FODMAP diet. Explore various international foods that cater to low FODMAP principles, such as Mexican rice bowls with grilled chicken or Thai dishes made with coconut milk. Always verify ingredients in sauces and avoid high FODMAP dressings.
Using a Low FODMAP Tracking App
Actionable tools like low FODMAP tracking apps can help in monitoring food intake and managing symptoms effectively. These apps typically feature large databases of foods categorized by FODMAP content. They enable users to learn about suitable meals and track personal experiences with reintroducing high FODMAP foods.
Key Takeaways
Following a low FODMAP diet can dramatically improve digestive health and well-being. Here are the main points to remember:
- Understand what constitutes a low FODMAP diet and personalize according to individual triggers.
- Create balanced meal plans focusing on delicious low FODMAP recipes.
- Engage effective cooking strategies and explore low FODMAP meal prepping.
- Communicate dietary needs clearly when dining out, and utilize resources for tracking.
FAQ
1. What foods are strictly prohibited in a low FODMAP diet?
High FODMAP foods to avoid include certain fruits like apples and pears, vegetables like garlic and onions, dairy products containing lactose, wheat products, and legumes. Always refer to a comprehensive low FODMAP food list to identify safe options.
2. How can I ensure I’m getting enough nutrients while on a low FODMAP diet?
To maintain nutritional balance, incorporate a variety of low FODMAP fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and nutritious grains. Consult a dietitian to help design a well-rounded meal plan and address potential nutrient gaps.
3. Is the low FODMAP diet suitable for children?
The low FODMAP diet can be adapted for children, especially those with digestive issues. It’s essential to involve a healthcare provider to customize the diet for developmental needs while ensuring they enjoy tasty low FODMAP recipes for kids.
4. How do I manage cravings for high FODMAP foods?
Use low FODMAP substitutes in your recipes to resolve cravings. Examples include using lactose-free cheese for dairy and gluten-free bread to replace baked goods. Sugary treats can have low FODMAP desserts to curb sweet cravings responsibly.
5. Can the low FODMAP diet help with weight management?
The low FODMAP diet can prevent digestive discomfort, often prompting some individuals to make healthier food choices naturally. Emphasizing fresh produce and lean proteins can lead to weight management success while also alleviating IBS symptoms.